Context: Recently, an Earthquake of magnitude 6.1 struck a rural, mountainous region of eastern Afghanistan. In this article we will try to know some basic information related to earthquake.
Causes of Afghanistan’s earthquake:
- Alpide belt:
- Afghanistan is earthquake-prone because it’s located in the mountainous Hindu Kush region, which is part of the Alpide belt.
- This belt is the second most seismically active region in the world after the Pacific Ring of Fire.
- The Alpide belt runs about 15,000 KM, from the southern part of Eurasia through the Himalayas and into the Atlantic. Along with the Hindu Kush, it includes a number of mountain ranges, such as the Alps, Atlas Mountains, and the Caucasus Mountains.
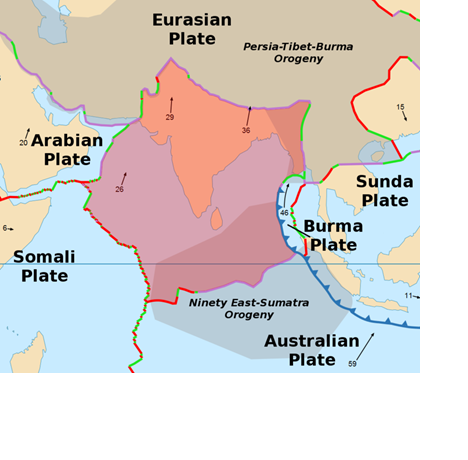
- Converging plates:
- The Earth’s crust is especially lively in Afghanistan because it is where the Arabian, Indian and Eurasian tectonic plates meet.
- The boundary between the Indian and Eurasian plates exists near Afghanistan’s border with Pakistan. Recent earthquake formed when the Indian plate crashed violently with the Eurasian plate. Collisions like this shake and squeeze the ground upwards. Along with causing earthquakes, this movement creates mountains like the Himalayas or the Hindu Kush and Pamir Mountain ranges in northeast Afghanistan.
About Earthquake:
- It is the shaking of the surface of the Earth which results in a sudden release of energy in the Earth’s lithosphere (rocky outer part of the Earth) that creates seismic waves.
- Earthquakes can cause severe damage, particularly in an area where homes and other buildings are poorly constructed, and landslides are common.
- An earthquake’s point of initial rupture is called its hypocentre or focus.
- The epicentre is the point at ground level directly above the hypocentre.
- It is measured in the Richter scale.
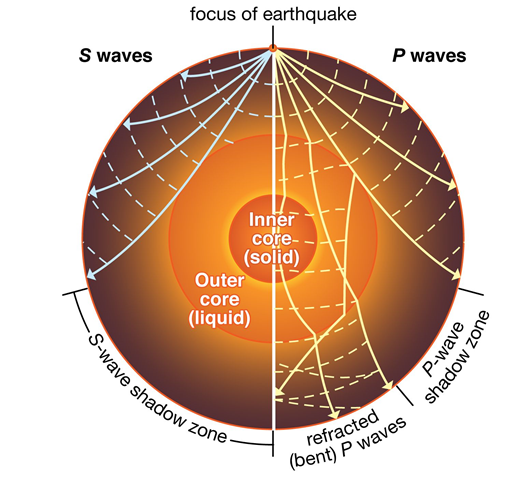
Earthquake waves
These are of 2 types – body waves and surface waves
- Body waves:
- These waves are generated due to the release of energy at the focus and move in all directions travelling through the body of the earth. Hence, the name-body waves. It travels only through the interior of the earth. It is faster than surface waves.
- There are 2 types of body waves: P- primary waves and S-secondary waves.
- P waves travel through gaseous, liquid, and solid materials whereas S waves travel only through solid materials.
- Surface Waves: When the body waves interact with surface rocks, a new set of waves is generated called surface waves. These waves move along the earth’s surface. Surface waves are transverse waves in which particle movement is perpendicular to the wave propagation. Hence, they create crests and troughs in the material through which they pass. These are the most damaging waves. Two common surface waves are Love waves and Rayleigh waves.
- Speed of different Waves in descending order: Primary Waves > Secondary Waves > Love Waves > Rayleigh Waves.
- Shadow Zones:
- There exist some specific areas where the waves are not reported. Such a zone is called the ‘shadow zone’. A zone between 105° and 145° from the epicentre (approximately) is identified as the shadow zone for both the types of waves.
Image Courtesy: Britannica.com
Earthquake Zones in India:
Zone II – Low risk zone (40.93% of India comes under this zone).
Zone III – Moderate risk Zone (30.79% of India comes under this zone).
Zone IV – High risk zone (17.49% of India comes under this zone).
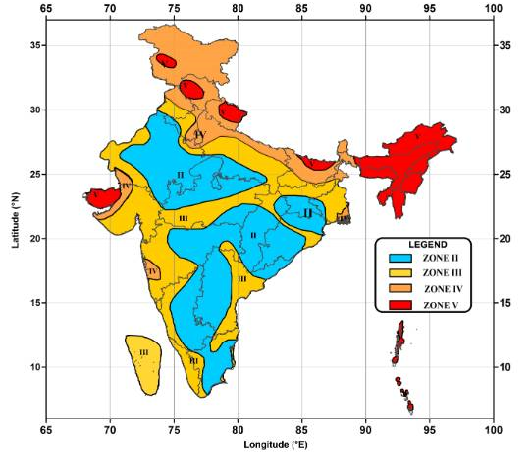
Zone V- Very high-risk zone (10.79% of India comes under this zone)
Image Courtesy: nidm.gov.in SEE HER