G-7 Summit 48th
Context- Recently, group of seven Countries (G-7) concluded its three-day summit in the Bavarian Alps of Germany in which Ukraine was assured humanitarian and economic assistance while other matters like climate change, food and energy security, health, gender rights and counter terrorism were also discussed.
Image Courtesy: g7germany/g7
Key outcomes of the G-7 Meet
- G7 stands firmly by Ukraine’s side for as long as it takes.
- G7 agrees to establish an open and cooperative Climate Club by the end of 2022 as a global response to the climate crisis.
- G7 takes further action to accelerate the international climate change agenda.
- G7 fights hunger crisis with “Alliance for Global Food Security”.
- G7 seeks to secure the supply of energy.
- G7 will develop global partnerships for infrastructure and investment.
- G7 agrees on global economy and inflation risks.
- G7 cooperates to strengthen global health.
- G7 underpins action based on shared values.
- G7 and partner countries Indonesia, India, Senegal, South Africa, and Argentina send out joint signal for the strengthening of resilient democracies.
G-7 Summit 48th
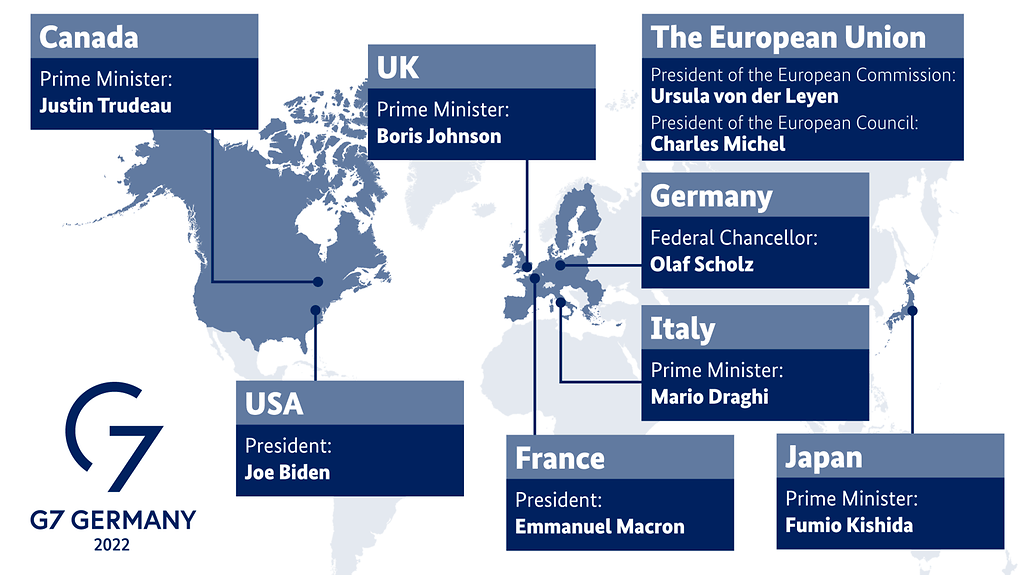
About G-7
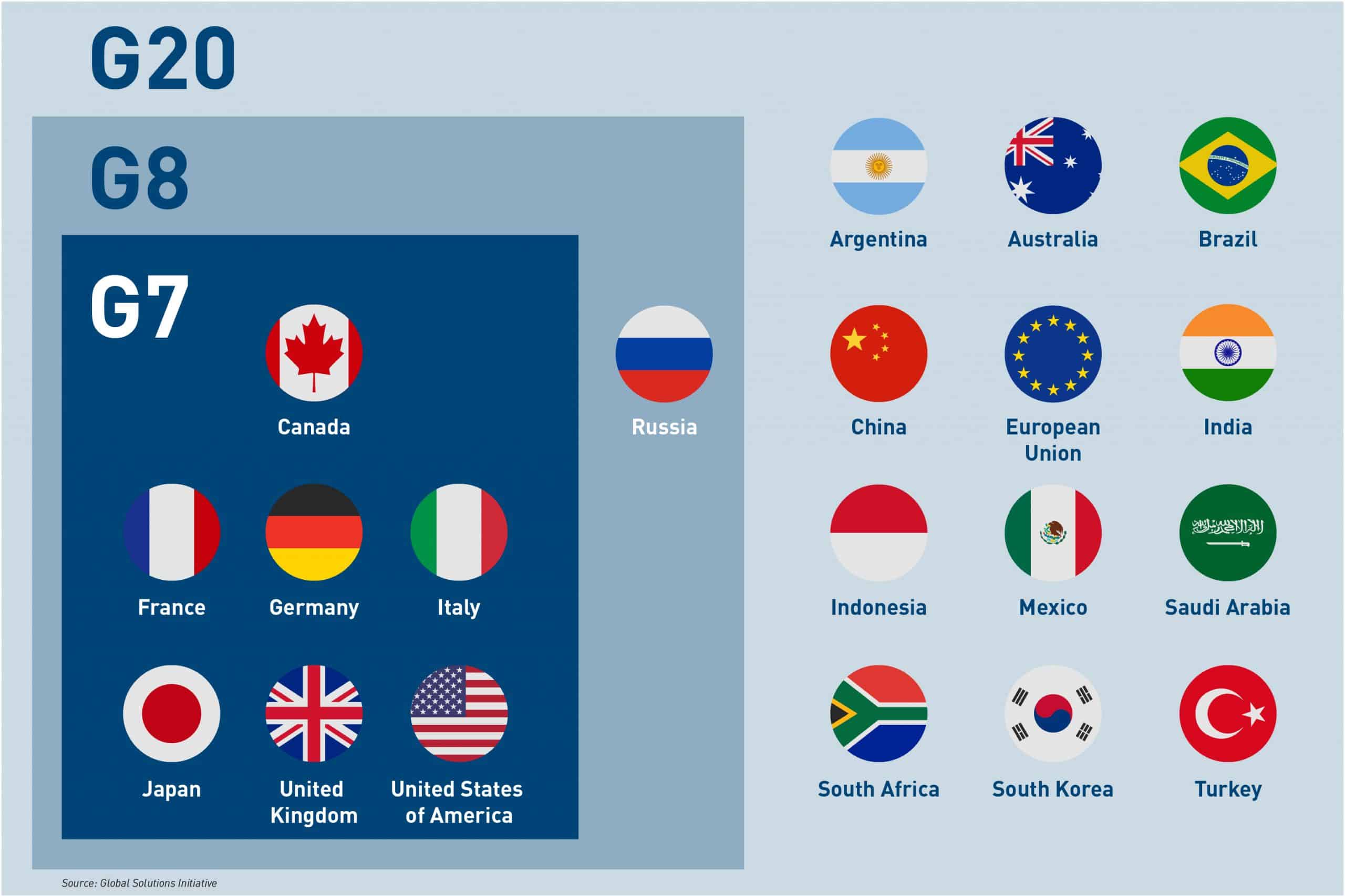
· The Group of Seven (G7) is an inter-governmental political forum. · Member countries are- Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom, and the United States. In addition, the European Union is a ‘non-enumerated member’. · Its members are the world’s largest IMF advanced economies and liberal democracies; the group is officially organized around shared values of pluralism and representative government. · All the G-7 and India are part of G-20. · The group regards itself as “a community of values”, with freedom and human rights, democracy, the rule of law, prosperity, and sustainable development as its key principles. · It meets annually to discuss issues of common interest like international security, energy policy and global economic governance. · It does not have a formal constitution, or a fixed headquarters and the decisions taken by leaders during annual summits are non-binding. G-7 Summit 48th
History G-7 Summit 48th· On 25th March 1973, in the backdrop of 1973 oil crisis, U.S. Secretary of the Treasury, George Shultz, convened an informal gathering of finance ministers from West Germany, France, and the United Kingdom before an upcoming meeting in Washington, D.C. · Meeting was held in its library and subsequently these four countries came to known as “Library Group”. · In 1973 IMF & World Bank proposed the addition of Japan. · The informal gathering of senior financial officials from the U.S., U.K., West Germany, Japan, and France became known as the “Group of Five”. · In November 1975, France hosted a three-day summit; invited the Group of Five plus Italy, forming the “Group of Six” (G6). · Cananda joined the Group in 1976 and it became “Group of Seven” or G-7. · European Union (EU) began attending the meetings from 1977. · Since started in 1994 Russian officials held separate meetings with leaders of the G7. This informal arrangement was dubbed the “Political 8” (P8) or G7+1. · In 1997, Russia became the official 8th member of grouping. · In March 2014, Russia precipitated an international crisis when it occupied and annexed Crimea, an autonomous republic of Ukraine. Hence G-7 responded by indefinitely suspending Russia’s membership in the group and the group became again G-7 from G-8. |
Issues cited by G7 countries
G-7 Summit 48th
- Russia’s income from oil sales is financing its invasion of Ukraine.
- High energy prices are a big problem for G-7 countries consumers.
- Higher global oil prices have softened the blow to Russia’s income even as Western traders shun Russian oil.
- Food Cost: West has become fatigued by the cost of a war that is contributing to soaring energy costs and price hikes on essential goods around the globe.
- Gold: The US says Russia has used gold to support its currency as a way to circumvent the impact of sanctions. One way to do that is by swapping gold for a more liquid foreign exchange that is not subject to current sanctions. Russia will still be able to sell gold to other countries outside the Group of Seven jurisdiction.
Impact on Russia
G-7 Summit 48th
- Isolate Russia economically: The gold import ban is meant to isolate Russia economically, starve its funding arm and prevent money laundering.
- Hit on funding: As western experts claim that the war in Ukraine is funded by Oil refiners in Russia, this move will hit on the war funding.
- Severe sanctions: The country’s richest have rushed to convert their assets into gold to avoid the impact of the financial restrictions.
Impacts on India
G-7 Summit 48th
- Inflation and crude prices: Further ban could lead to rising oil prices, further posing risk to India’s rising inflation. India imports more than 80 per cent of its oil requirement, but the share of oil imports in its total imports is around 25%. Rising oil prices will also impact the current account deficit (the difference between the values of goods and services imported and exported).
- India’s diplomatic dilemma: Because of India’s strategic ties with Russia and its dependence on Russia for military supplies 60 to 70% of India’s military hardware is of Russian-origin.
- Impact on Indian exports: Russia is India’s 25th largest trading partner with exports of $2.5 billion and imports of $6.9 billion. India’s key exports to Russia include mobile phones and pharmaceuticals while India’s key imports from Russia are crude oil, coal, and diamonds. Tea is a major export item from India.
- Clean Energy: Clean energy provides a variety of environmental and economic benefits, including a reduction in air pollution. A diverse clean energy supply also reduces the dependence on imported fuels. Renewable clean energy also has inherent cost savings, as there is no need to extract and transport fuels, such as with oil or coal, as the resources replenish themselves naturally.
- Statement on international order: The statement assumes significance amidst aggressive moves by China in the strategic Indo-Pacific region as well as Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. India, the US, and several other world powers have been talking about the need to ensure a free, open and thriving Indo-Pacific in the backdrop of China’s aggressive military manoeuvring in the region. China also claims nearly all of the disputed South China Sea, though Taiwan, the Philippines, Brunei, Malaysia, and Vietnam all claim parts of it. Beijing has built artificial islands and military installations in the South China Sea.
Source: The Hindu & g7germany.org SEE HER